Model Context Protocol (MCP) - How to use the ADOxx MCP server
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open standard that describes how large language models (LLM) can connect with external tools, systems and data sources to have access to context-specific information (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Model_Context_Protocol, https://modelcontextprotocol.io/introduction).
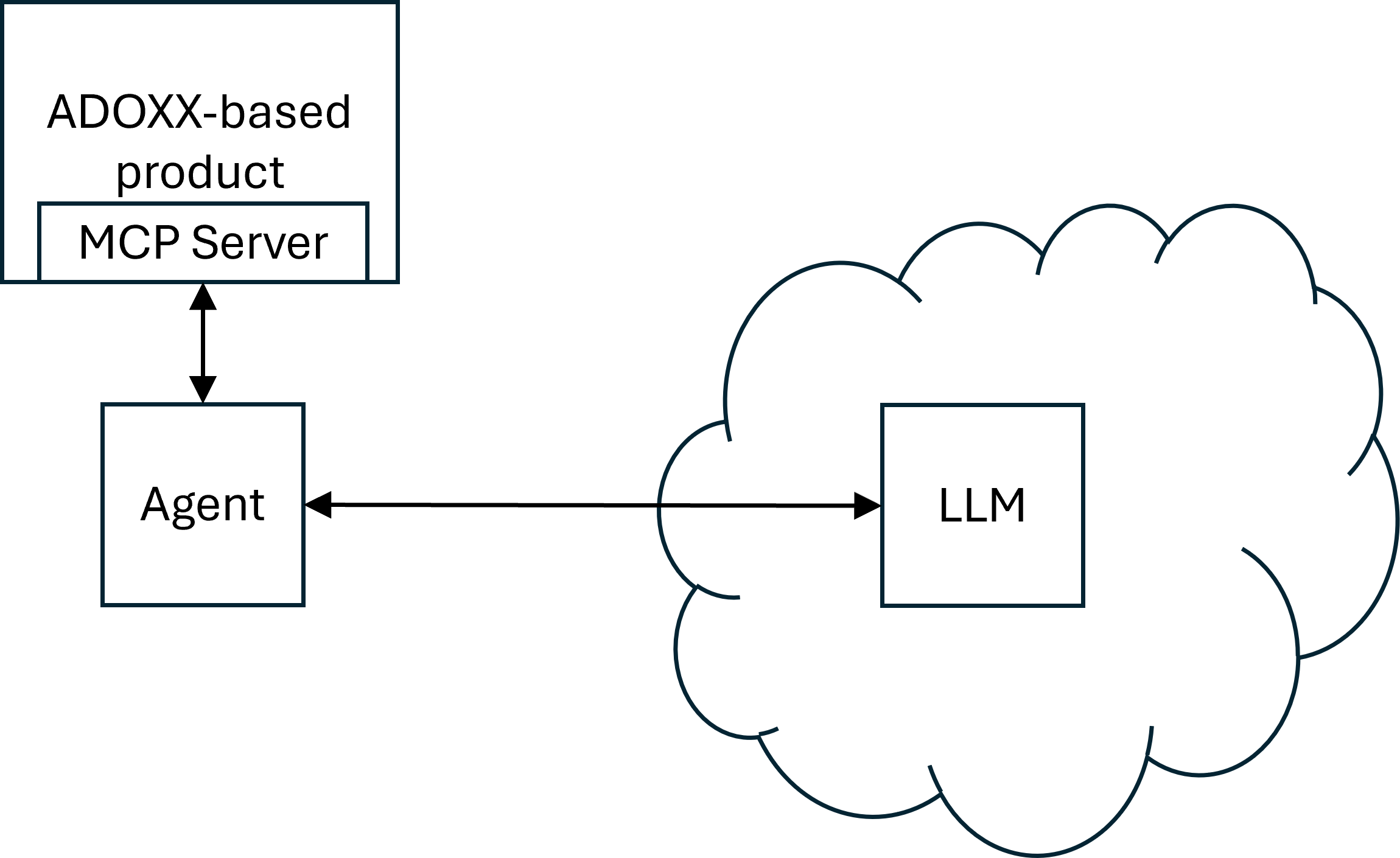
This article shows how the ADOxx MCP server can be generally contacted and how a Python agent backed by an LLM (in this case OpenAI) can be implemented that accesses the ADOxx MCP server via streamable HTTP to use the configured tools.
For information on how to create your own MCP server that uses ADOxx as a tool provider, see https://developer.boc-group.com/adoxx/en/mcp_rest/.
ADOxx MCP Server
With version 29.5, ADOxx contains an MCP server component that is available at /mcp/message and can be accessed using streamable HTTP. For documentation on how to activate and configure the MCP server component, refer to MCP.
The ADOxx MCP server provides access to a set of configured tools depending on the used product and specific configuration. For more details, contact your account manager. The tool "_getRepositories" is always available and will provide the list of repositories for the user that accesses the MCP server.
Testing the availability of the ADOxx MCP Server
To test the availability of the ADOxx MCP Server, tools like Postman, Bruno or curl can be used. As the communication between an MCP agent and the server is done using streamable HTTP, HTTP requests can be used to make sure that the ADOxx MCP Server is up and running.
Initialization
A simple request to the ADOxx MCP Server can be done by sending an HTTP request using the following data:
- URL: <ADOXX_URL>/mcp/message (e.g. http://host:8080/ADOxx/mcp/message)
- Method: POST
- Authentication: Either basic authentication or OAuth 2.0 authentication, based on the configuration within the product.
- Headers:
- Content-Type: application/json
- Accept: application/json, text/event-stream
- Body:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 0,
"method": "initialize",
"params":
{
"protocolVersion": ""
}
}
This should produce a response with HTTP status 200 and a body containing information about the server and the available MCP protocol. It should also contain a header named mcp-session-id whose values is the MCP session ID that should be used for subsequent requests to the ADOxx MCP Server.
Listing available tools
To do a subsequent request that lists the available tools, an HTTP request with the following data can be sent:
- URL: <ADOXX_URL>/mcp/message (e.g. http://host:8080/ADOxx/mcp/message)
- Method: POST
- Authentication: Either basic authentication or OAuth 2.0 authentication, based on the configuration within the product.
- Headers:
- Content-Type: application/json
- Accept: application/json, text/event-stream
- mcp-session-id: The MCP session ID produced by the initialize request
- Body:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 2,
"method": "tools/list",
"params":
{
"_meta":
{
"progressToken": 2
}
}
}
This should produce a cresponse with HTTP status 200 and a body containing text consisting of the MCP session ID, the type of event (message) and a section data, which contains a JSON object describing the available tools.
Sample Agent implementation
IMPORTANT: These is an exemplary scenario to show how the ADOxx MCP server can be used. For sake of simplicity and compactness, the code described in this article uses Basic authentication and passwords in clear text in configuration files.
The description and files documented in this article are an exemplary scenario to serve as a starting point for implementing specific MCP scenarios.
In a productive scenario, it is required to adapt the provided example to follow the usual best practices and standards such as using OAuth 2.0 for authentication, not storing cleartext passwords, etc.
Here, we will create an agent in Python that is backed by OpenAI and accesses the ADOxx MCP server using Basic authentication (The MCP server supports both Basic and OAuth 2.0 authentication).
In the agent, a user can then write a request which will be forwarded to the LLM.
In case the request matches one of the provided tools, the LLM will instruct the agent to call the tool.
The agent will provide the tool's result to the LLM which processes it further (e.g. by presenting it to the user).
Prerequisites
To run this example, the following prerequisites have to be met:
- The contents of the directory https://github.com/BOC-Group/developer-examples/tree/master/howto/mcp has to be downloaded to a local directory.
- Python has to be installed. For this example, Python 3.11.9 was used.
- pip, the package installer for Python has to be installed. It can be installed along with Python.
- The required libraries listed in https://github.com/BOC-Group/developer-examples/blob/master/howto/mcp/requirements.txt have to be installed using pip. pip is Python's package installer and usually contained in the Python installation directory in the subfolder Scripts. Install the requirements by executing
pip install -r requirements.txt
- An ADOxx-based product (based on ADOxx 29.5) has to run and a user has to be available that can access https://developer.boc-group.com/adoxx/en/rest-repositories/#/Repository%20read%20APIs/getRepo via Basic authentication
- The MCP Server has to be configured and enabled (see MCP)
- The agent has to be configured to access the MCP Server endpoint (/mcp/message) and use an OpenAI LLM by adding the necessary information in the file https://github.com/BOC-Group/developer-examples/blob/master/howto/mcp/.env:
- OPENAI_API_KEY: A key to access Open AI's API (This example uses Open AI's LLM, but it can be adapted to use any other LLM that supports Function Calling can be used).
- adoxx_username: The name of a user that can use the REST API using Basic authentication
- adoxx_password: The password of a user that can use the REST API using Basic authentication
- adoxx_url: The base URL of the product installation (e.g. http://host:8080/ADONIS or http://host:8080/ADOIT)
Writing the Agent
The agent is the Python program that runs locally and processes the communication from the user and to the LLM.
The code for the agent is contained in https://github.com/BOC-Group/developer-examples/blob/master/howto/mcp/agent.py
When executed, the agent will ask the user for its input and then process it. The agent will access the ADOxx MCP server at the configured URL with the provided credentials using Basic authentication. It will access the OpenAI LLM using the openai Python library:
Click to view the code!
async def main():
try:
username = os.environ.get("adoxx_username");
password = os.environ.get("adoxx_password");
token = base64.b64encode(f"{username}:{password}".encode()).decode()
headers = {"Authorization": f"Basic {token}"}
openai_client = AsyncOpenAI()
except Exception as e:
logging.error("Error during initializing the client: %s", e)
print(f"Error during initializing the client: {e}")
try:
async with streamablehttp_client(
f"{ADOXX_URL}/mcp/message",
headers=headers
) as (reader, writer, get_session_id):
logging.info("Connected to server")
try:
async with ClientSession(reader, writer) as session:
await session.initialize()
tools_response = await session.list_tools()
tools = tools_response.tools
functions = []
for tool in tools:
function = {
"name": tool.name,
"description": tool.description,
"parameters": tool.inputSchema
}
functions.append(function)
print(f"tool: {tool.name}")
messages = [{
"role": "system",
"content": (
"You are a specialized assistant that supports tool use for interacting with a BOC metamodel and data repository. "
"Only use general knowledge if no suitable tool is available."
"IMPORTANT: If you respond using general knowledge and not a tool, explicitly state this at the beginning of your reply "
"by saying: 'Answer based on general knowledge — no tool was used.'")}]
while True:
user_input = input("User: ")
if user_input.strip().lower() == "exit":
print("Terminating the conversation...")
break
messages.append({"role": "user", "content": user_input})
Agent Usage
To use the scenarios, the necessary parameters in the file .env have to be set and the product has to run.
To start the agent, execute
python agent.py
This will result in the agent starting up and waiting for user input.
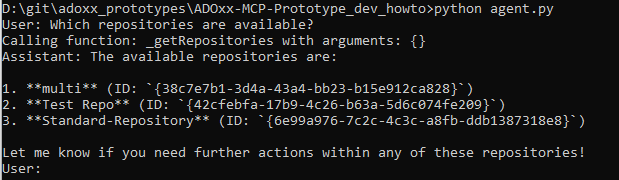
Input can be provided by asking for the available repositories, e.g. "Which repositories are available?"
This should result in the agent contacting the LLM which will use the tool "_getRepositories". Whenever a tool is called, this is shown by the agent on the console:
Logging
Logs are created in the subfolder logs. There are two different types of log files:
- agent_<TIMESTAMP>.log: Contains information related to the agent, e.g. errors when trying to reach the LLM, http requests sent to the LLM or when calling functions.
- messages_<TIMESTAMP>.json: Contains the messages that are sent or received by the agent.